Overview
I built a self-hosted Kubernetes homelab to experiment with DevOps best practices, automate infrastructure management, and self-host personal applications. This setup allows me to test new technologies in a controlled environment while maintaining full control over my data.
Goals
🔹 Running Kubernetes on low-power, low-cost hardware.
🔹 Automating deployments using GitOps.
🔹 Managing secrets and configurations securely.
🔹 Balancing cost-efficiency and high availability.
Solution & Implementation
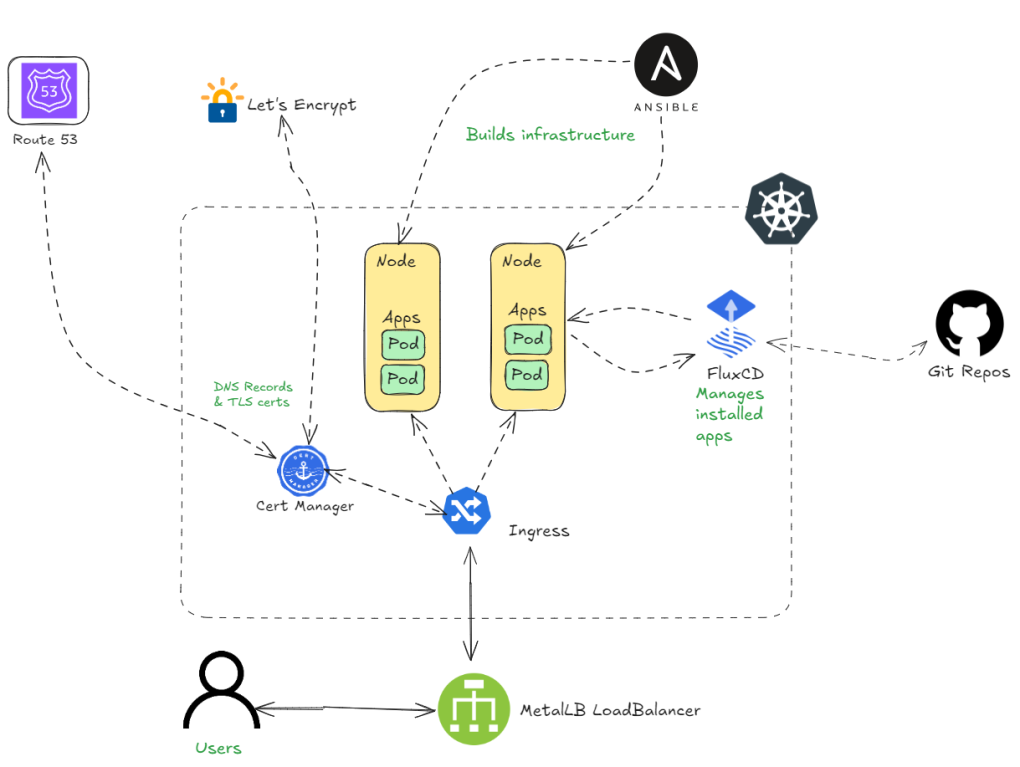
Set up two Kubernetes clusters:
- – Production Cluster on physical hardware (HP 635, MacMini)
- – Staging cluster on Hyper-V virtual machines
- Deployed applications using FluxCD GitOps workflows.
- Automated infrastructure provisioning with Ansible.
- Managed secrets securely using AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store.
- Used AWS Route 53 for DNS management.
- Implemented NGINX Ingress & MetalLB for traffic routing.
- Adopted best practices in security, backups, and maintenance.
Tech Stack
K3s (Kubernetes) | FluxCD | Ansible | AWS Route 53 | AWS Parameter Store | NGINX Ingress | MetalLB | Ubuntu Linux | Let’s Encrypt | Cloudflare Tunnels
Outcome
- Fully automated deployments via GitOps.
- Reliable and cost-effective self-hosted infrastructure.
- Secure secret management using AWS Parameter Store.
- Ability to experiment freely without cloud costs.
Code
🔗 GitHub Repo: github.com/terrameijar/homelab-infrastructure
Lessons Learned
🔹 Optimizing Kubernetes for low-resource hardware.
🔹 Using GitOps workflows with FluxCD for automated deployments.
🔹 Using Ansible for infrastructure automation.
🔹 Managing multi-cluster setups effectively.